Rosacea Is Chronic But Also Quite Treatable
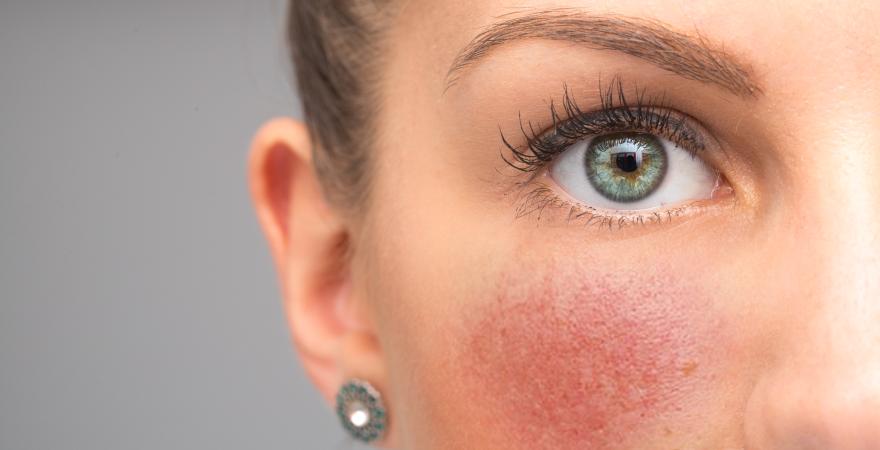
Rosacea is a chronic disorder that affects approximately 16% of the population but is most common in those aged 20-49. It usually appears on the face and can manifest as redness, flushing, swelling, and bumps or pimples. It can also appear on other body parts, like the chest and back. Rosacea has a genetic component, so it's not uncommon for rosacea to be passed down from parents to their children. The severity of rosacea varies greatly, with some people only experiencing problematic symptoms occasionally while others have a lifelong occurrence that ranges from mild to severe. There are several types of rosacea, including the following: Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (ETR) is the most common type, characterized by flushing and persistent redness. Papulopustular rosacea (PPR) is marked by bumps or pimples with itching, burning, stinging, and inflammation. Eye rosacea affects the eyes with symptoms like burning, stinging, itching and tearing.
Causes of Rosacea
There are several reasons in which a person might develop rosacea. The common causes include:
- Hormonal Changes - Hormonal changes are often linked to rosacea flare-ups. It could be because the human body is sensitive to small fluctuations in hormones, and when it reacts, it results in skin redness due to blood vessels dilating. When hormonal levels constantly rise and fall, the body's natural response is to try and maintain its blood flow by creating more red blood cells. When these levels constantly change, the body can't keep up with its natural rhythm, causing it to "fight itself."
- Inflammatory Factors - Unhealthy lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol, and stress can cause rosacea symptoms. In addition, the elements in the environment can also aggravate or trigger the disorder by causing an inflammatory response. It may be caused by exposure to sunlight or spicy food.
- Age - Rosacea tends to arise young; most cases don't appear until one's 30s/40s. However, if you're experiencing symptoms of rosacea now, it's more common for your child to develop it even though they haven't yet reached 30 years.
Signs and Symptoms of Rosacea
The most common sign of rosacea is redness on the face. Usually, the nose appears red, but it can also extend to your cheeks and forehead. The redness may be localized to one area or spread across your face. Sometimes some small bumps or pimples accompany the symptoms of rosacea.
Flushing is not considered a separate type of rosacea, but it may be a reaction to flare-ups or an independent occurrence. Flushing of the skin involves areas near the flush typically appearing pink, whereas other spots may have a pale color instead. The flushing is often accompanied by a warm feeling that can extend to the upper body, neck and ears.
Swelling is a symptom of rosacea that only affects the nose. It may develop gradually over time, or it can appear suddenly as a reaction to another condition, such as angioedema. The swelling on your nose comes with increased skin temperature, redness and burning sensation.
Another common sign of rosacea is bumps and pimples on the nose. Other symptoms like burning, itching and stinging usually accompany them.
Treating Rosacea
There are several ways in which to treat rosacea. The method used will depend on medical advice from a profession. Some of the options include:
- Antibiotics - Antibiotics are often prescribed to those dealing with rosacea. These come in the form of pills, ointments, and gel. Antibiotics work well on the bumps that develop on the skin, plus it's excellent at managing skin redness. It's important to note that antibiotics are primarily for bacterial infections, so do not take them if you've recently developed a bacterial infection.
- Topical Creams - Topical creams are applied to the skin to help reduce redness and swelling brought on by rosacea. They come in various forms that you apply directly to your skin.
- Antibacterial Substances - Antibacterial is applied to the skin to help treat redness and swelling by rosacea. It may be used twice daily until your skin is clear, but it should be used at most twice a day because long-term use can damage your eyesight and cause irritation.



